Overview of SynTrac Disciplines

Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is the study of the movement of air and other gases and their interaction with solid bodies. It studies flow patterns, forces and pressure distributions that occur when moving through the air and is crucial for the design of airplanes, cars and other vehicles in order to improve efficiency and stability. In SynTrac, one example is the joint optimization of propellers and laminar blades, where interactions of flow effects are used as efficiently as possible.

Acoustics
Acoustics is the science of sound. It studies the generation, propagation and perception of sound waves in various media. Through its analysis and control, it optimizes acoustic properties in rooms, reduces noise in machines and vehicles, and improves sound quality in audio technology. Applications include building acoustics, noise control and sound measurement technology. In SynTrac…. an example of this is the consideration of the balance between the efficiency of the new SynTrac technologies and the associated noise generation in the cabin and the environment. Optimizing this contributes significantly to the social acceptance of the proposed solutions.

Flight physics
Flight physics is the study of the physical principles that enable aircraft to fly. It includes lift, thrust, drag and weight, as well as the interactions of these forces. By analyzing aerodynamics, fluid mechanics and materials science, flight physics helps to develop safer and more efficient aircraft. In SynTrac, one example is the combination of thrust generation and control
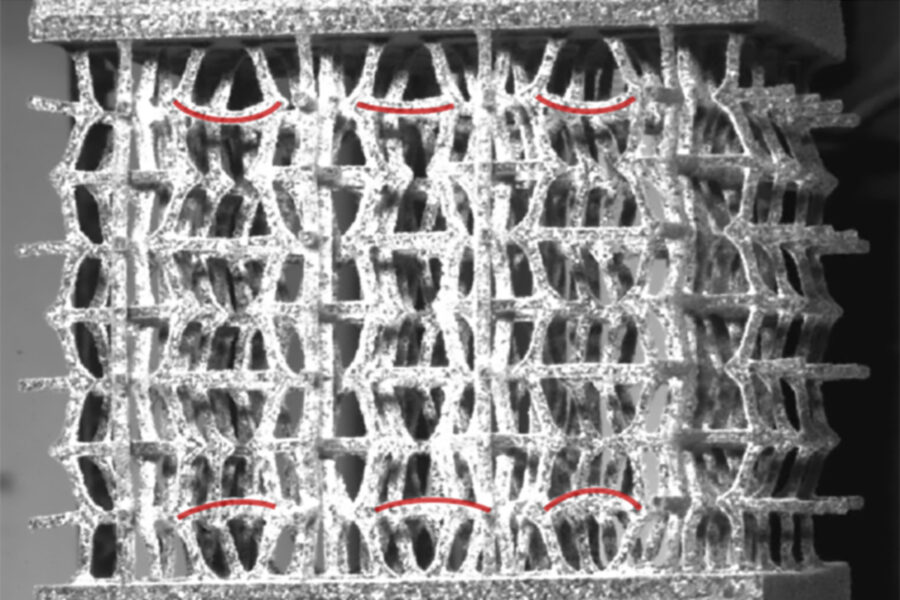
Structural mechanics
Structural mechanics examines the behavior of solid bodies under load and analyzes stresses, deformations and stability of structures. It uses the laws of statics and dynamics to design safe and efficient machines that can withstand the expected loads. One example of this in SynTrac is the suspension of the drive system in the aircraft structure. In SynTrac, the currently dominant division of tasks between engine and aircraft manufacturers is viewed as an integrative task and pursues the integration of the propulsion system into the fuselage structure.
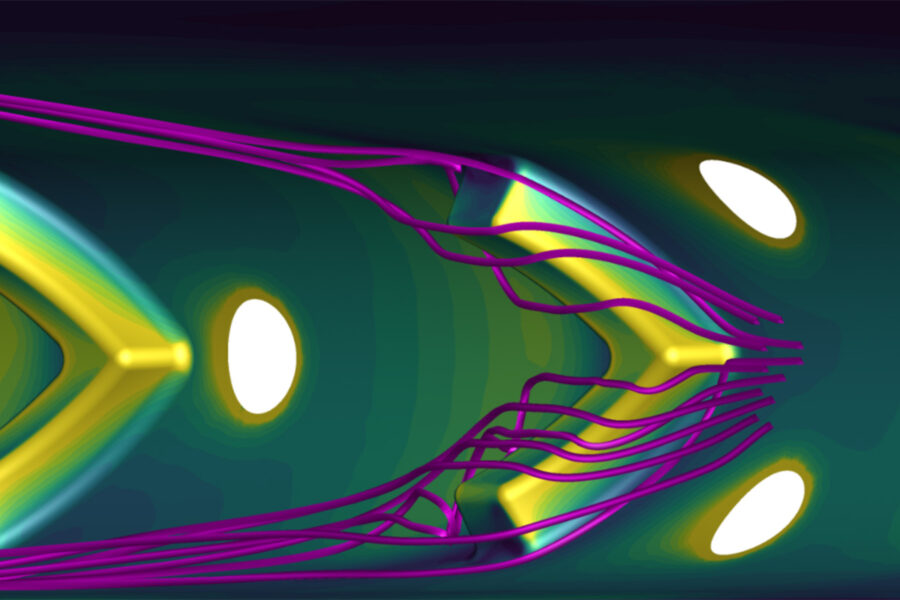
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics deals with energy, its conversion and the associated processes. It examines the principles that determine the behavior of macroscopic systems consisting of many particles, particularly with regard to temperature, heat and work. In SynTrac, one example of this is the targeted integration of propulsion systems into the aircraft structure through the use of suitable media in such a way that contrails are reduced, thereby significantly reducing the environmental impact.




